
While there is a conception that equipment leasing is not licensed, it is not quite true. Most states have license requirements, and all have issues on usury, requiring a sales/use tax permit, corporation filing to do business in a state, as well as many states have personal property license requirements from the owner of the equipment.
It is true that there are no state or national associations that regulate the industry as banks and other financial institutions or accountants, attorneys, realtors, to name a few. The closest may be the Certified Leasing Professional Foundation where they are 215 individuals that have passed a test, an annual test, and abide by a set of rules and regulations.
In most states, banks are not required to have a leasing license as well as manufacturers. Banks are generally exempt because they are regulated by the FDIC.
The common thread among licensing statutes is that if the entity which should otherwise have a license, is licensed by another government agency (real estate brokers is one example), then no license is required.
An expert on this who has won cases against company’s not licensed in California, notably CMC Commercial Credit, Tom McCurnin, Barton, Klugman & Oetting, Los Angeles, California told Leasing News: “A property owner can sell his property on credit without a license or without usury issues. Its called the Time Price Doctrine or Time Price Differential.
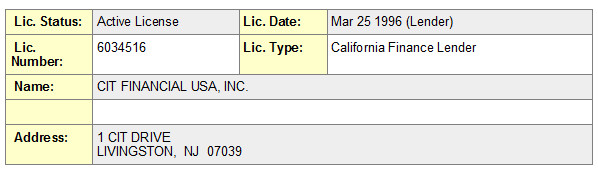
“CIT on the other hand doesn't own the stuff and is therefore making a loan and is required to have a license.
“A gray area might be for the leasing company to buy the stuff and have it shipped to them, and they, in turn re-ships to the customer. May not be required to have a license. Simple invoices and drop shipping probably would not pass muster.”
Captive Lessors are required to have a license, and all those that I checked do, such as Dell, who also sells other products than the ones they manufacture.
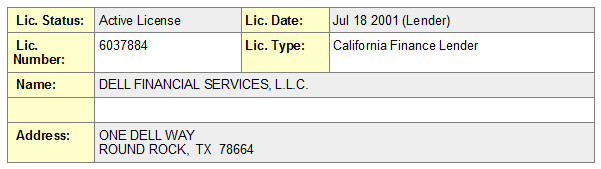
And while there are financial institutions that also have a bank, such as CIT, they hold a license.
In California, those engaged in true leases, such as Mar Vista, address, do not need to be licensed, but everyone who is involved in “capital leases” with a bargain purchase option, particularly a dollar, are required to be licensed. Without it, they may not accept a commission, engage with a licensed financial institution, and may find their leases in court dismissed for lack of a license. While the fines are not very much, the clout comes in immediate suspension from doing business in California, and while a hearing may be required or filed by an attorney, they may not engage in business during this time.
“NO BROKERAGE COMMISSIONS TO UNLICENSED BROKERS. California Administrative Code Title 10 §1451.”
Commissions may not be paid to unlicensed brokers. There are companies who use other companies’ documents and therefore believe they do not need to be licensed. This may be accurate in dealing with a bank, but not with another licensed financial institution or financial institution out of state that is not licensed in California.
If you are registered by license as a broker, lender, lessor in states that require it, you do not need a city business license (in most states). Cities that require a business license, also require a business license if you work out of your residence. Many cities now are using Schedule C from tax returns, such as in San Jose, California, to catch those without a city license, and they will go back several years as well as a fine, so best to get a license now in case they check your city.
While not all states require a lender's license, many require a license to accept a deposit or advance rental. And remember, a capital lease may be considered a loan as it is with the IRS in many states. If the state requires a license, and your company is not licensed, the transaction may be subject to usury laws.
46 states do not require the lessor to notify the lessee regarding the end of the original term of the lease and can invoke an Evergreen clause, except in these states that do require notification and if not, can void the residual as well as bring on a fine or worse, depending on the number of such transactions and complaints received.
States who require notification:
New York
Rhode Island
Texas
Wisconsin
Illinois
(In Illinois, Consumer law, but may affect commercial, especially a proprietorship, partnership or personal guarantee)
--Christopher Menkin
---Current Regulations
(Any up-dates or additions, please send
to kitmenkin@leasingnews.org)
Arizona: All "advance fee loan brokers" must register annually with the state. Includes "commitment fees." Stiff penalty and on line form for a complaint for the state to investigate. Arizona Revised Statutes, sec. 06-1303-1310 (1996)
Registration process: http://www.azdfi.gov/Licensing/Licensing-FinServ/ALB/ALB.html
Arkansas: All brokers of "a loan of money, a credit card or a line of credit" may not assess or collect an advance fee. In addition, all brokers must register with the Securities Commissioner, post a surety bond of $25.000 and have a net worth of $25,000.
Arkansas Code Annotate sec. 23-39-401 (1995)
California: "In addition to the lending authority provided by the law, the California Finance Lenders Law provides limited brokering authority. A "broker" is defined in the law as "any person engaged in the business of negotiating or performing any act as broker in connection with loans*made by a finance lender." Brokers licensed under this law may only broker loans to lenders that hold a California Finance Lenders license."
http://www.corp.ca.gov/Laws/Finance_Lenders/Default.asp
(*any transaction that is not a true rent or meets the accounting and tax rules or is re-sold as a loan or discount or has a nominal purchase option is considered under this nomenclature. ) (2)
Florida: Brokers of a "loan of money, a credit card, line of credit or related guarantee, enhancement or collateral of any nature" may not assess or collect an advance fee.
Florida Statues, Chapter 687.14 (1992)
Georgia: A broker of "loans of money, a credit card, a line of credit or related guarantee, enhancement or collateral of any kind or nature" may not assess or collect an advance fee unless such fee is for "actual services necessary to apply for the loan." Official Code of Georgia Annotated, sec. 7- 7-1 (1992)
Idaho: No fee may be collected unless a loan is actually made.
Idaho Code, sec. 26-2501 (1992)
Illinois: Code, 815 ILCS 175/15-5.03 Under the Act, a" loan broker" means any person who, in return for a fee from any person, promises to procure a loan for any person or assist any person in procuring a loan from any third party, or who promises to consider whether or not to make a loan to any person. 815ILCS 175/15-5- 15(a) specifically excluded from the application of the Act, however, are (1) any bank …regulated by any service loans for the Federal National Mortgage Association… (3) any insurance producer or company authorized to do business in [Illinois], (4) any person arranging financing for the sale of the person's product, (note that this exception does not apply to any person selling someone else's product and only applies to "the" person's product, implying the exception is for the owner of the product arranging for financing), (5) any person authorized to conduct business under the Residential Mortgage License Act of 1987 and (6) any person authorized to do business in [Illinois] and regulated by the Department of Financial Institutions or the Office of Banks and Real Estate. "In the event that the Act is violated by the broker, the Secretary of State is empowered by the statute to make investigations and examinations, suspend or revoke the broker's approval, subpoena witnesses, compel the production of books and records, order depositions and obtain temporary restraining orders and injunctions against the broker. In the vent that a violate is found, the Secretary of State may impose a fine in the amount of $10,000 for each violation and the broker shall be liable to any person damaged in the amount of tactual damages plus attorneys’ fees." This appears as standard language on most states.
Iowa: A broker of loans of "money or property" may not assess or collect an advance fee except for a "bona fide third-party fee" and a broker must obtain a bond or establish a trust account and file required documents with the Commissioner or Insurance.
Iowa Code, sec. 535C (19920)
Kansas : Broker is not exempt. Discounter or Lessor is exempt: " 'Creditor' means any person to whom a loan is initially payable on the face of the note or contract evidencing the loan" is exempt. Anyone who earns a fee or accept a deposit, except a bank, financial institution, discounter or lessor, must be registered.
http://www.securities.state.ks.us/rules/loan.rtf
Kentucky: Brokers of "a loan of money, a credit card, a line of credit or related guarantee, enhancement or collateral of any kind or nature" may not assess or collect an advance fee.
Kentucky Revised Statutes Annotated, sec. 367.380 (1992)
Louisiana: A broker of loans of "money or property…whether such agreement is styled as a loan, a lease or otherwise" must obtain a surety bond or establish a trust account in the amount of $25,000. A broker may not collect an advance fee but may collect an "advance expense deposit for commercial loans" only for actual expenses incurred in obtaining the loan. Louisiana Revised Statutes Annotated, sec. 9:3574 (1993); Louisiana Revised Statutes Annotated, Sec. 51:1910 (1992)
Non-Louisiana leasing companies, with or without offices in the state, must qualify to do business in Louisiana, and are subject to payment of state and local occupational license fees. See: Collector of Revenues v Wells Fargo Leasing Corp., 393 So.2d 1255 (La. App. 1981). Common misunderstanding of Louisiana law. Motor vehicle lessors, with or without offices in Louisiana, additionally are required to be licensed by the Louisiana Motor Vehicle Commission in order to lease a motor vehicle in the state. (La. R.S. 32:1254(N)) Common misunderstanding of Louisiana law.
Maine: No license required: "the regulation of commercial loan brokers does not fall under the jurisdiction of the Maine Bureau of Consumer Credit Protection. Transactions involving two businesses are legal/contractual in nature. Therefore, disputes involving a commercial loan between a business and commercial loan provider or broker must be settled in the court system."
http://www.maine.gov/pfr/consumercredit/faqs/loan_broker_faq.htm#j
Mississippi: A broker or loans of money may not assess or collect an advance fee and can be fined up to $5,000 for each violation. Mississippi Code Annotated, sec. 81-19-17 (1997)
Missouri: A broker of loans of "money or property" may not assess or collect an advance fee. Missouri Revised Statues, sec. 367 300 (19920
Nebraska: A broker of loans of money may not assess or collect an advance fee. Nebraska Revised Statutes, sec. 45-189 (1993)
New Hampshire
Any person making small loans, title loans, or payday loans in New Hampshire must obtain a license from the bank commissioner. N.H. Rev. State. Ann. § 399-A:2. This law does not apply to banks, trust companies, insurance companies, savings or building and loan associations, or credit unions. Id. Any person who violates any provision of this chapter shall be guilty of a misdemeanor if a natural person, or a felony if any other person. N.H. Rev. Stat. Ann § 399-A:18.
New Jersey: Brokers of "loans of money" may not assess or collect an advance fee.
New Jersey Rev. Statutes, sec. 17:10B (1992)
Although New Jersey does not require a lessor to obtain a license to conduct a leasing business in the state, the New Jersey Corporation Business Activities Report Act requires foreign corporations to register with the state. See N.J. STAT. ANN. 14A:13-14. In particular, foreign corporations must file a Notice of Business Activities Report with New Jersey's Department of Taxation. Activities that trigger the requirement of a report include: (a) maintaining an office or other place of business in New Jersey; (b) maintaining personnel in New Jersey, even if the personnel is not regularly stationed in the state; (c) owing or maintaining real or tangible personal property directly used by the corporation in New Jersey; (d) owning or maintaining tangible and/or property in New Jersey used by others; (e) receiving payments from residents in New Jersey, or businesses located in New Jersey, that are greater than $25,000.00; (f) deriving any income from any source or sources within New Jersey; or (g) conducting or engaging in any other activity, property or interrelationships with New Jersey as may be designated by the Director of the Division of Taxation. See N.J.S.A. 14A:13-15. Corporations not required to file a report are those which either received a certificate of authority to do business, or filed a timely tax return under the Corporation Business Tax Act, or Corporation Income Tax Act. See N.J. STAT. ANN. 14A:13-16. Reports must be filed annually by April 15th.
Nevada: Foreign Corporations Foreign corporations engaged in activities in Nevada are subject to the provisions of Chapter 80 of the Nevada Revised Statutes. Specifically, NRS 80.010 through 80.055 set forth the requirements for a foreign corporation to qualify to do business in Nevada. Of primary importance are the statutes that establish (a) the filing requirements to qualify to do business (NRS 80.010); (b) the activities in which a foreign corporation may engage that do not constitute “doing business” so as to require qualification (NRS 80.015); and (c) the penalties to which a foreign corporation will be subject for failing to comply with the qualification provisions (NRS 80.055). The penalties for failure to comply with the qualification statutes include a fine (capped at $10,000) and/or denial of the right to maintain a court action. However, failure to comply will not impair the validity of contracts entered into by a foreign corporation nor prevent such corporation from defending itself in court. Foreign LLCs Foreign LLCs engaged in activities in Nevada are subject to the provisions of Chapter 86 of the Nevada Revised Statutes, specifically NRS 86.543 through 86.549. Foreign LLCs seeking to operate in Nevada must comply with the initial filing and registration requirements in NRS 86.544, and annual filing requirements of NRS 86.5461. The LLC must also maintain certain records, such as a list of current members and managers, in accordance with NRS 86.54615. Additionally, NRS 86.5483 lists the activities which do not constitute “doing business” in Nevada for purposes of the Chapter. Foreign LLCs that fail to comply with the Chapter risk penalties similar to those facing a non-compliant foreign corporation. Those penalties are outlined in NRS 86.548.
New Mexico: New Mexico currently requires Brokers/Lessors to register for Licensing under the NM Mortgage loan Company or Loan Broker Act with the Financial Institutions Division of the State of New Mexico. Banks with Brick and Mortar within the State of New Mexico are exempt. Prior to licensing applicants must submit the Following:
Articles of Incorporation
Listing of all principals (including management)
A full financial Package (to meet their minimum requirements of liquidity)
Personal financial statements on all principals
Disclosure of all current or past suits (civil or criminal)
Attach a corporate surety bond
Include a $400.00 registration fee renewable yearly
North Carolina: A broker of "loans of money or property…whether such agreement is styled as a loan, a lease or otherwise" must obtain a surety bond or establish a trust account in the amount of $25,000 and obtain a license. North Carolina General Statutes, sec. 66-106 (1992)
North Dakota: Brokers may not accept an advance fee unless the broker is licensed. North Dakota Century Code, 13-04. 1-09.1 (1993) Ohio: Department of Commerce, Division of Financial Institutions
(Certificate to engage in the business of a credit services organization in accordance with the provisions of Sections 4712.01 to 4712.14 of the revised code of Ohio, subject to all the provisions thereof and to the regulations of the division.) Ohio Department of Taxation requires a "Vendor's License" under provision 5739.17 of the Revised Code (...is hereby authorized to sell tangible personal property and selected services at the retail location specified below.) This also makes the lessor responsible for all taxes with penalties for not doing so.
Ohio: Ohio law provides that no person may engage in the business of lending money, credit, or choses in action in amounts of $5,000 or less, or exact, contract for, or receive, directly or indirectly, on or in connection with any such loan, any interest and charges that in the aggregate are greater than the interest and charges that the lender would be permitted to charge for a loan of money if the lender were not a licensee, without first having obtained a license from the Division of Financial Institutions. O.R.C. 1321.02. This rule is applied to any person, who by any device, subterfuge, or pretense, charges, contracts for, or receives greater interest, consideration, or charges than that authorized by such provision for any such loan or use of money or for any such loan, use, or sale of credit, or who for a fee or any manner of compensation arranges or offers to find or arrange for another person to make any such loan, use, or sale of credit. O.R.C. 1321.02.
Rhode Island: Any person who acts as a lender, loan broker, mortgage loan originator, or provides debt-management services must be licensed. R.I. Gen Laws § 19-14-2(a). The licensing requirement applies to each employee of a lender or loan broker. R.I. Gen Laws § 19-14-2(b). No lender or loan broker may permit an employee to act as a mortgage loan originator if that employee is not licensed. R.I. Gen Laws § 19-14-2(b) R.I. Gen. Laws § 19-14-2 (2012) No person engaged in the business of making or brokering loans shall accept applications from any lender, loan broker, or mortgage loan originator who is required to be licensed but is not licensed. R.I. Gen Laws § 19-14-2(d). There is an exemption from the licensing requirement for a person who makes not more than 6 loans in the state within a 12-month period. R.I. Gen Laws § 19-14.1-10. Persons lending money without a license are guilty of a misdemeanor and can be fined not more than $1,000, or imprisoned for not more than 1 year, or both; each violation constitutes a separate offense. R.I. Gen Laws § 19-14-26.
South Carolina: A broker of "a loan of money, a credit card, a line of credit or related guarantee, enhancement or collateral of any kind or nature" may not assess or collect an advance fee. South Carolina Code Annotated, sec. 34-36-10 91992)
South Dakota: Money Lending License
Required for individuals or corporations to engage in the business of lending money, including creating and holding or purchasing and acquiring any installment loan ("Capital Lease" or EFA), single pay loan, or open-end loan which may be unsecured or secured by personal property. Requires filing a surety bond application. State and national banks, bank holding companies, other federally insured financial institutions, and the subsidiaries of those institutions are exempt from licensure. In addition, SD chartered trust companies are exempt from licensure. Any individual or corporation holding this license is required to pay the bank franchise tax.
Duration: 1 year
Cost: Application $600
Vermont: Commercial Loans
Commercial loan license would apply to EFA and "Capital Leases." Exemptions include transactions over $1 million, and brokers who do not engage in transactions more than $50,000 in one year at rates not exceeding 12 percent per annum.
Ontario, Canada: General Requirements: 1. Branch Operation If a foreign corporation wants to carry on business via a branch operation, without a Canadian corporate entity, it may have to obtain a provincial license in each province in which it intends to carry on business. Pursuant to the Ontario Extra-Provincial Corporations Act R.S.O. 1990 c. E.27 ("EPCA"), a class 3 extra-provincial corporation (a corporation that has been incorporated or continued under the laws of a jurisdiction outside Canada) is prohibited from carrying on business in Ontario without a license under the Act [s. 4(2)]. Failure to comply with this licensing requirement can lead to a maximum fine of $2,000 for a person and $25,000 for a corporation [s. 20(1)]. Directors, officers and any person acting as a representative of the corporation can be fined up to $2,000 for authorizing, permitting or acquiescing to an offence by the corporation [s. 20(2)]. For the purposes of the EPCA, an extra-provincial business is considered to be "carrying on business in Ontario" if: a. It has a resident agent, representative, warehouse, office or place where it carries on its business in Ontario; b. It holds an interest, otherwise than by way of security in real property situate in Ontario; or c. It otherwise carries on business in Ontario [s. 1(2)]. This last category is a catchall. Recent case law in the area stresses that it is very much a fact-specific analysis hinging on the extent to which business is actually conducted in Ontario. 2. Incorporation: a foreign corporation can also choose to incorporate a subsidiary, either federally or provincially. If a subsidiary is incorporated provincially in Ontario, it may have to obtain an extra-provincial license to carry on business in other provinces. An Ontario-incorporated company does not have to obtain a license to carry on business in Quebec but does have to make annual information filings. 3. Bank Act If the financing company is a bank and intends to carry on business in Canada, it must obtain appropriate approval under the Bank Act 1991 c. 46. Whether an entity will be considered a bank under the Bank Act needs to be reviewed on a case-by-case basis, as there are a number of relevant factors.